As artificial intelligence moves beyond predictive tasks and content generation, a new class of systems is emerging, popularly known as Agentic AI. Unlike traditional AI, which reacts to input and operates within limited boundaries, agentic AI demonstrates autonomy, planning, and decision-making. It does not merely respond to prompts; it takes initiative to accomplish objectives.
Agentic AI is increasingly becoming central to next-generation enterprise systems, AI research, and real-world automation. This article explains what agentic AI is, how it differs from earlier models, where it is applied, and why it matters.
Defining Agentic AI
Agentic AI refers to systems capable of pursuing high-level goals autonomously by combining reasoning, memory, environmental awareness, and tool use. These systems do not operate as isolated models; rather, they function as agents, capable of interpreting instructions, creating plans, executing tasks, and adapting as situations change.
For example, an agentic AI assigned a task like “schedule a business trip” can independently search flights, compare options, check calendar conflicts, and send confirmations, without requiring step-by-step instructions from a human. The process involves multiple stages like goal interpretation, task decomposition, tool integration (such as APIs), and continuous feedback monitoring.
This form of reasoning and execution is called agentic reasoning, where the AI makes ongoing decisions based on outcomes and new information, all in service to a predefined goal.
How Agentic AI Differs from Traditional AI
Traditional AI models, including machine learning classifiers and even many large language models, are reactive. They produce outputs in response to specific inputs and rely heavily on human users to frame tasks, interpret outputs, and execute real-world actions.
Agentic AI, by contrast, exhibits initiative. It sets sub-goals, autonomously uses tools or APIs, and monitors its own progress. The distinction can be summarized as follows: 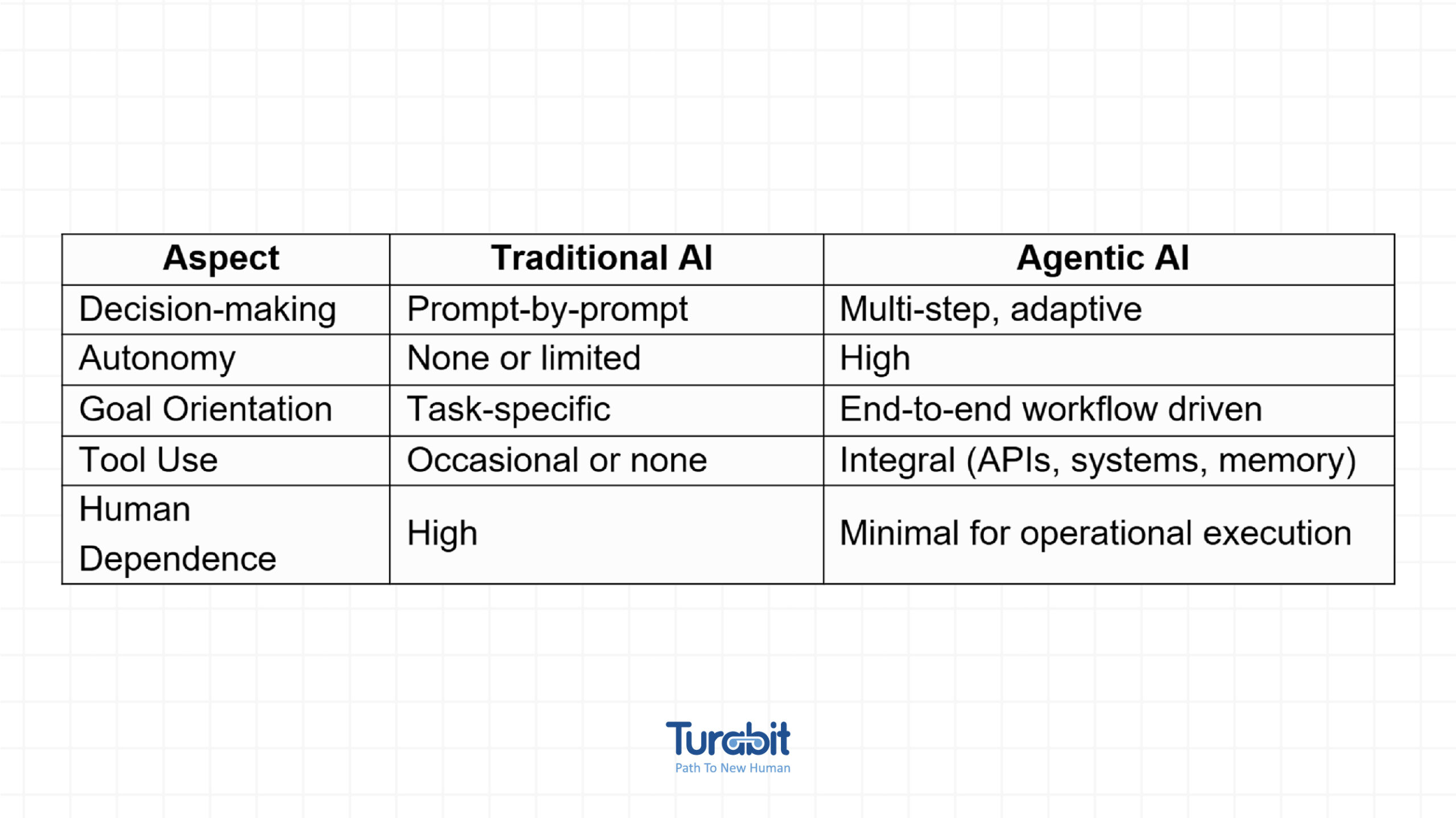
Practical Applications Across Domains
Agentic AI is already being adopted across a wide spectrum of industries and domains. It enables systems that go beyond task execution, instead of managing entire workflows. Key applications include:
Here are keyways automation powers proactive CX:
Enterprise Process Automation
Organizations are deploying agents that monitor KPIs, generate business reports, manage approvals, and reconcile accounts. These agents are integrated with CRMs, ERPs, and business intelligence systems to automate multi-step processes with little or no human involvement.
Customer Service
AI agents are used to triage customer support requests, fetch account data, provide resolutions, and follow up, all without escalation to human agents. This reduces response times, increases resolution accuracy, and improves customer experience while reducing operational costs.
Software Development
Developer-facing agentic systems assist not just with code generation, but with debugging, writing tests, and deploying applications. Agents can read documentation, infer requirements, and make decisions in context, thereby speeding up delivery and reducing error rates.
Healthcare and Finance
In clinical and financial environments, agents can sift through vast amounts of data to generate summaries, highlight anomalies, and initiate follow-up actions. They help in scheduling, compliance monitoring, and decision support for professionals operating in high-stakes domains.
Marketing and Sales Automation
Agentic AI systems manage content pipelines, test variations, analyze campaign performance, and optimize strategies over time. Marketing teams use them to personalize communication and automatically manage outreach across multiple channels.
These use cases demonstrate the broad utility of agentic AI across knowledge-intensive, repetitive, and multi-system workflows.
Benefits of Agentic AI
The operational and strategic advantages of agentic AI are considerable. Key benefits include:
Autonomy and Efficiency: By handling end-to-end processes, agents reduce the need for constant human supervision. This leads to time savings and cost reduction across roles and departments.
Scalability and Flexibility: Agentic systems can operate simultaneously across use cases, geographies, and time zones. They can scale horizontally, managing dozens or hundreds of concurrent tasks with consistent quality.
Proactive Decision-Making: Unlike reactive systems, agents plan and make decisions based on evolving data and user intent. This allows organizations to move from responding to events to anticipating them.
Improved Human-AI Collaboration: With agents taking over repetitive tasks, human employees can focus on strategy, creativity, and oversight. This raises productivity while improving job satisfaction.
Tool and System Integration: Modern agent frameworks allow seamless integration with APIs, internal tools, and third-party systems, enabling full automation across ecosystems rather than isolated tasks.
Conclusion
Agentic AI marks a significant evolution in the field of artificial intelligence, transforming systems from static tools to autonomous, goal-driven agents. As this technology matures, it offers organizations the ability to scale operations, enhance decision-making, and unlock new efficiencies across functions.
However, deploying agentic systems responsibly requires a strong foundation in oversight, ethics, and governance. For technology leaders, now is the time to evaluate where and how agentic AI can bring real value, while putting the right safeguards in place.

