IT operations inside SaaS businesses require precision, speed, as well as resilience. The rapid flow of customer requests, infrastructure dependencies, and compliance requirements demand automation at multiple support layers.
Yet the challenge lies in separating what belongs to Level 1 (L1) automation and what qualifies for Level 2 (L2). Without this distinction, organizations either under-automate or misapply automation where human intervention is still vital.
This analysis explains the operational roles of L1 and L2 automation, their differences, and direct use cases in SaaS businesses.
Understanding L1 IT Automation
L1 automation addresses repetitive, predictable, and high-frequency tasks. These are the requests and incidents that do not require specialized analysis but instead follow a defined workflow. SaaS environments generate an abundance of such tasks, especially when scaling across multiple users and tenants.
Characteristics of L1 Automation
• Volume-driven: High number of requests with low complexity
• Rule-based execution: Predefined scripts or workflows
• No deep context required: Minimal or no business-specific investigation
• Immediate resolution potential: Tasks can be completed in seconds
Core Functions in SaaS
• Password resets: Automated credential recovery systems eliminate IT helpdesk dependency
• Account provisioning and deprovisioning: Scripts manage user lifecycle with strict logging
• Access requests for standard tools: Automation engines validate entitlement rules and grant access
• Health monitoring alerts: Automated restart or remedial action when CPU spikes or services lag
• License allocation: Automatic assignment of licenses when new employees join
L1 automation reduces service desk costs and speeds up resolution by removing dependency on manual handling for routine problems.
Understanding L2 IT Automation
L2 automation deals with problems that exceed predefined workflows but remain solvable through structured logic and advanced automation. These issues often involve correlation of multiple data points, advanced decision-making, and system-level orchestration.
Characteristics of L2 Automation
• Moderate to high complexity: Requires diagnostic steps, not just execution
• Contextual dependency: Must analyze multiple factors before applying a fix
• Cross-system orchestration: May trigger actions across several tools
• Failure handling: Includes fallback mechanisms when automated resolution is not possible
Core Functions in SaaS
• Root cause identification: Automated event correlation to trace repeated service interruptions.
• Dynamic resource allocation: Automated scaling of cloud infrastructure during spikes.
• API error remediation: Intelligent monitoring detects integration failures and executes corrective workflows.
• Patch automation with validation: Deploying security patches across environments after pre-checks.
• Incident triage: AI-assisted automation categorizes, prioritizes, and routes incidents with recommendations.
L2 automation does not remove humans entirely. Instead, it reduces workload on higher-skilled IT teams by resolving recurring mid-level incidents or preparing incidents with structured diagnostics for faster handling.
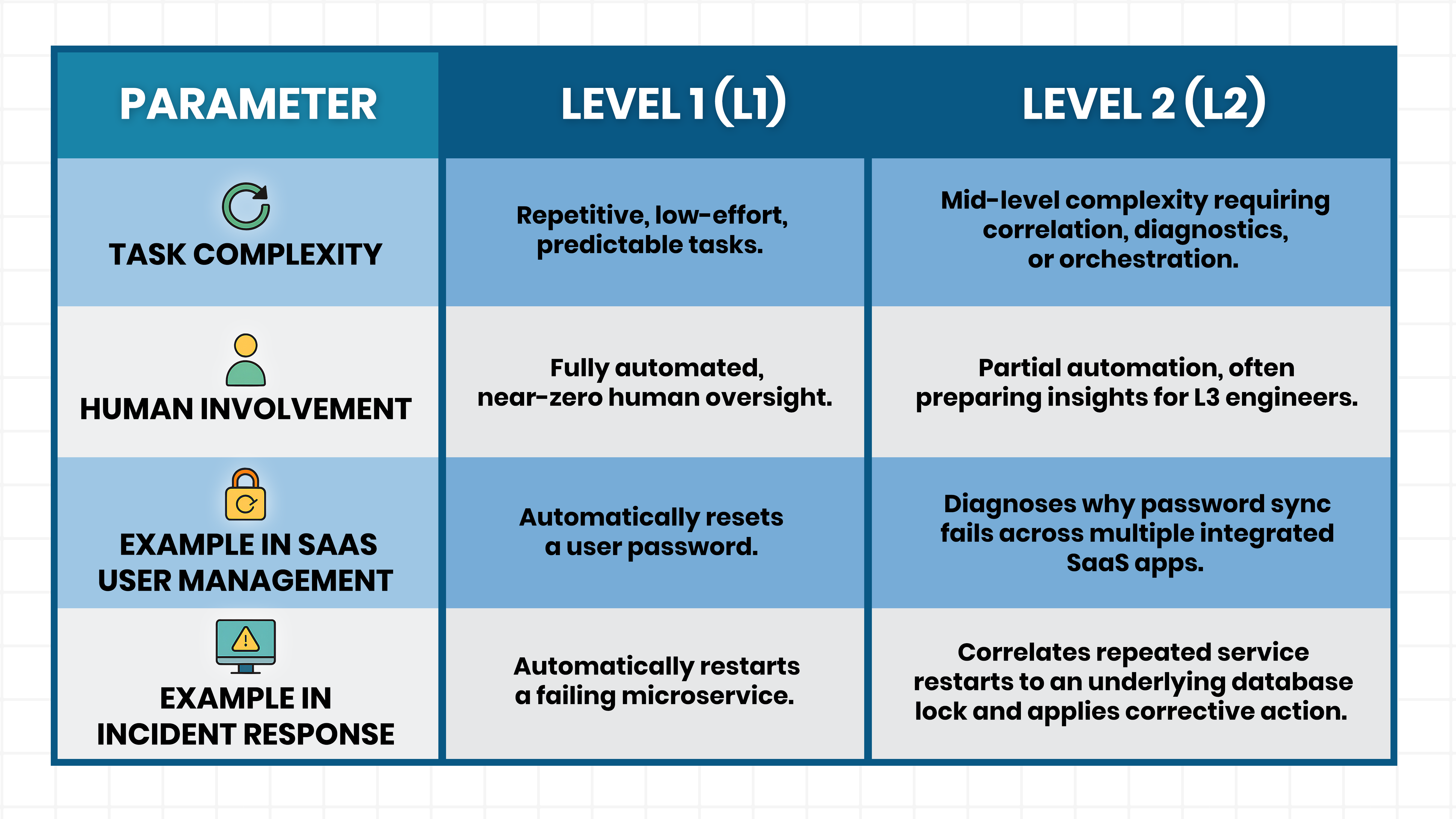
Key Differences Between L1 and L2 Automation
These differences prevent overlap. L1 scales efficiency, while L2 creates resilience.
Some Use Cases of L1 Automation in SaaS
1. User Lifecycle Management
Automated provisioning and deprovisioning ensure compliance and speed during employee onboarding or exits. Scripts validate role-based access and update across connected SaaS platforms.
2. Knowledge Article Delivery
AI assistants serve predefined solutions to end users without agent intervention. Frequently asked issues, like “How to connect VPN?” are resolved instantly.
3. Basic Service Health Remediation
Simple auto-healing workflows restart services or clear cache when triggered by monitoring alerts.
4. License and Subscription Allocation
L1 AI Assistants handle repetitive license assignments, reducing licensing delays and preventing service interruptions.
Use Cases of L2 Automation in SaaS
1. Multi-System Failure Correlation
When multiple SaaS integrations fail simultaneously, L2 automation performs log correlation, identifies the triggering source, and applies corrective workflows.
2. Security Incident Response
Automated quarantine of suspicious user accounts after detecting abnormal login patterns, combined with alert escalation to security engineers.
3. Advanced Capacity Management
Scaling workloads in Kubernetes or cloud VMs after analyzing traffic patterns across services.
4. Compliance Patch Automation
Automated patch deployment in production systems with rollback capability if performance drops.
5. Application Integration Error Handling
Automatically reprocessing failed API calls after validating endpoint health, minimizing downtime.
Business Benefits of Separating L1 and L2 Automation
Separating L1 and L2 automation creates clarity in execution and impact. It ensures routine issues are resolved instantly while more complex challenges are systematically addressed, delivering measurable business outcomes.
Here is why separating L1 and L2 automation is advantageous for your business.
• Operational Efficiency: L1 absorbs routine workload, reducing ticket volume at the helpdesk.
• Faster Recovery: L2 minimizes downtime during service-impacting incidents.
• Cost Optimization: High-volume L1 automation reduces labor cost, while L2 reduces loss from outages.
• Scalability: SaaS firms scale globally without proportional increase in IT headcount.
• Compliance Strengthening: Automated logs maintain audit trails across both layers.
Strategic Approach for SaaS Businesses
Separating L1 and L2 automation creates a structured path for scaling IT efficiency. It ensures routine tasks are fully automated while higher-level workflows benefit from guided orchestration and oversight.
• Begin with L1 automation maturity: password resets, provisioning, license management
• Progress into L2 orchestration: root cause identification, advanced security automation, API error correction
• Maintain human oversight: ensure fallback controls exist for critical business systems
• Continuously measure automation ROI: track reduction in MTTR (mean time to resolve) and IT workload
Conclusion
A clear distinction between L1 and L2 automation ensures SaaS businesses apply automation with precision. L1 drives efficiency for high-volume tasks, while L2 strengthens resilience for complex incidents. Together, they optimize costs, improve reliability, and enable IT teams to focus on innovation that sustains long-term growth and competitiveness.

